Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Swalloing Disorders
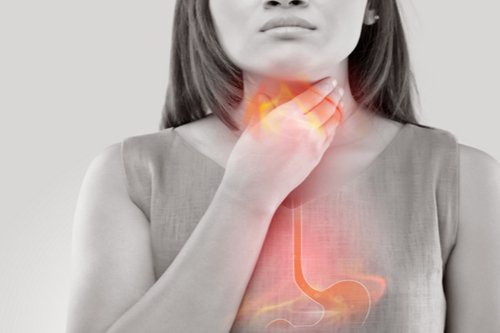
Swallowing disorders, also known as dysphagia, refer to difficulties or abnormalities in the process of moving food, liquids, or saliva from the mouth to the stomach. Dysphagia can result from various underlying causes and may affect different stages of the swallowing process. Common signs and symptoms of swallowing disorders include coughing or choking during meals, pain while swallowing, regurgitation, weight loss, and recurrent respiratory infections.
Dysphagia is the medical term for swallowing difficulties. Some people with dysphagia have problems swallowing certain foods or liquids, while others can’t swallow at all. Other signs of dysphagia include: coughing or choking when eating or drinking.
Types of Swallowing Disorders
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Difficulty in the initial phases of swallowing, involving the mouth and throat.
Causes: Neurological disorders (e.g., stroke, Parkinson’s disease), muscle weakness, structural abnormalities, or damage to the nerves controlling swallowing.Esophageal Dysphagia: Difficulty in the later phases of swallowing, primarily involving the esophagus.
Causes: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), esophageal strictures (narrowing), tumors, or motility disorders affecting esophageal muscles.
Symptoms of Swallowing Disorders:
- Choking or Coughing: Especially during or after eating.
- Pain or Discomfort: While swallowing or in the chest.
- Regurgitation: Food or liquids coming back up.
- Weight Loss: Due to difficulty in consuming an adequate amount of food.
- Change in Voice: Sometimes associated with aspiration of food into the airway.
Common Causes of Swallowing Disorders
- Structural Issues:
- Tumors: Growths in the mouth, throat, or esophagus can impede the normal swallowing process.
- Diverticula: Pouches that form in the walls of the esophagus may cause difficulties in food passage.
- Muscle Weakness:
- Aging: Natural aging can lead to muscle weakness, including those involved in swallowing.
- Myasthenia Gravis: An autoimmune disorder affecting muscle strength.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders:
- GERD: Chronic acid reflux can damage the esophagus and cause swallowing problems.
- Achalasia: Impaired esophageal motility due to a malfunctioning lower esophageal sphincter.
Treatment for Swallowing Disorders
Speech-Language Therapy:
- Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP): SLPs play a key role in assessing and treating dysphagia. They may conduct evaluations, recommend specific exercises to improve muscle strength and coordination, and teach compensatory strategies to enhance swallowing safety.
Dietary Modifications:
- Texture Modification: Adjusting the texture of foods and liquids to make them safer to swallow. This could involve changes such as moving to a softer diet, pureed foods, or thickened liquids.
- Nutritional Management: Ensuring adequate nutrition through dietary adjustments, supplements, or, in severe cases, alternative feeding methods.
Positional Changes:
- Postural Adjustments: Changing the position of the head, neck, or body during meals to facilitate safer swallowing.
- Chin Tuck Technique: Tucking the chin to the chest during swallowing to protect the airway.
Swallowing Maneuvers:
- Supraglottic Swallow: Involves taking a breath, holding it, swallowing, and then coughing to clear the airway.
- Mendelsohn Maneuver: A technique to enhance the opening and closing of the upper esophageal sphincter during swallowing.
Medical Interventions:
- Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, medications may be prescribed to address issues such as acid reflux or muscle weakness.
- Botulinum Toxin (Botox): In certain cases, Botox injections may be used to relax specific muscles causing swallowing difficulties.
Surgical Options:
- Dilation: Widening a narrowed esophagus through endoscopic procedures.
- Myotomy: Surgical cutting of muscles to relieve tension or spasm.
- Fundoplication: Surgical procedure to address severe gastroesophageal reflux.
