Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Electromyography EMG
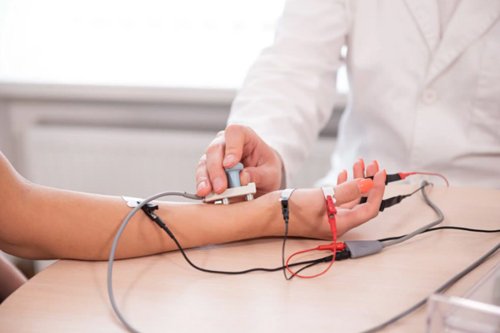
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the health and functioning of muscles and the nerves controlling them. It involves the measurement and recording of the electrical activity generated by muscle cells during contraction and at rest. EMG is often performed by neurologists, physiatrists, or trained technicians to evaluate neuromuscular disorders, identify nerve dysfunction, and assess muscle activity.
In needle EMG, fine, sterile needles are inserted into specific muscles to record the electrical activity. The needles pick up signals from the muscle fibers and provide information about the function of the muscles and the nerves supplying them.Surface EMG involves the placement of adhesive electrodes on the skin overlying the muscles being studied.
Reasons why EMG may be needed
Diagnosis of Neuromuscular Disorders:
- EMG is crucial in diagnosing a variety of neuromuscular conditions, including:
- Peripheral neuropathies (nerve damage)
- Radiculopathies (compression or inflammation of nerve roots)
- Myopathies (muscle disorders)
- Motor neuron diseases (e.g., amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or ALS)
- Neuromuscular junction disorders
- EMG is crucial in diagnosing a variety of neuromuscular conditions, including:
Localization of Nerve or Muscle Damage:
- EMG helps identify the location and extent of nerve or muscle damage. This information is essential for determining the cause of symptoms and planning appropriate treatment.
Assessment of Nerve Conduction:
- Nerve conduction studies (NCS) are often performed alongside EMG to assess how well nerves conduct electrical signals. This is valuable in identifying nerve dysfunction or damage.
Differentiation Between Nerve and Muscle Disorders:
- EMG aids in differentiating between disorders primarily affecting nerves and those primarily affecting muscles. This differentiation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Evaluation of Motor Neuron Diseases:
- EMG is an essential tool in evaluating conditions that affect motor neurons, such as ALS. It helps in monitoring disease progression and planning supportive care.
Electromyography Procedure
EMG Procedure:
If EMG is deemed necessary based on the evaluation, the procedure will be scheduled. During the EMG, the patient may undergo needle EMG and/or nerve conduction studies (NCS).
Needle EMG: Fine needles are inserted into specific muscles, and the electrical activity is recorded both at rest and during muscle contraction. This provides information about the health of the muscles and the nerves controlling them.
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Small electrical stimuli are applied to assess how well nerves conduct electrical signals. This helps identify nerve damage or dysfunction.
Results Interpretation:
- A trained healthcare professional interprets the results of the EMG, looking for patterns or abnormalities in the electrical activity. Abnormal findings can provide valuable information about the presence and nature of neuromuscular conditions.
Diagnosis:
- Based on the results of the EMG, a diagnosis is made. The healthcare provider will discuss the findings with the patient and formulate a treatment plan.
Treatment Options:
- Treatment plans vary depending on the specific diagnosis. Some common treatment options for neuromuscular conditions identified through EMG may include:
- Physical therapy or rehabilitation exercises to strengthen muscles.
- Medications to manage symptoms or address underlying causes.
- Occupational therapy to improve daily functioning.
- Surgical interventions, if necessary, to address nerve compression or other structural issues.
- Lifestyle modifications to manage and improve overall health.
