Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Nerve conduction study
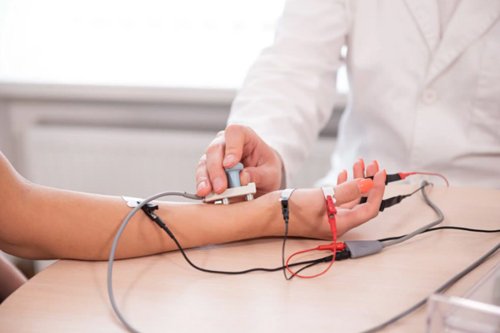
A Nerve Conduction Study (NCS) is a diagnostic test used to evaluate the function and health of peripheral nerves—nerves located outside the brain and spinal cord. This study is often performed in conjunction with Electromyography (EMG), and the combined test is referred to as an EMG/NCS.
NCS is conducted to assess the electrical conduction of signals along the nerves. It helps identify abnormalities in nerve function, such as nerve damage, compression, or other disorders affecting the peripheral nervous system.Minimal preparation is usually required. The patient may be asked to avoid using creams or lotions on the skin on the day of the test, as these can interfere with the electrical conductivity.
What does a nerve conduction study diagnose?
Peripheral Neuropathies:
- NCS is commonly used to diagnose and characterize peripheral neuropathies. Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain. Common causes include diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- NCS is often used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome, a condition characterized by compression of the median nerve at the wrist. This can result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
Radiculopathies:
- Radiculopathy refers to compression or inflammation of nerve roots as they exit the spinal cord. NCS can help identify radiculopathies, which may cause pain, weakness, and sensory disturbances in specific areas of the body.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome:
- Guillain-Barré syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that affects peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis. NCS is used to confirm the diagnosis by detecting abnormal nerve conduction.
How does a nerve conduction study work?
1. Preparation:
- The patient is prepared for the test by removing any clothing or accessories that might interfere with the placement of electrodes. The skin over the areas where nerves will be tested is cleaned to ensure good electrical contact.
2. Electrode Placement:
- Electrodes are placed on the skin over specific points along the course of the nerve being studied. These electrodes are typically adhesive patches or surface electrodes. Some studies may involve needle electrodes for more precise measurements.
3. Stimulation:
- A mild electrical stimulus is applied to the skin over the nerve using one of the electrodes. The stimulus generates an electrical impulse that travels along the nerve.
4. Recording:
- Another electrode, placed at a specific distance from the stimulation point, records the electrical response generated by the nerve. This response is called the action potential.
5. Measurement:
- The NCS measures two main parameters:
- Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV): This measures how quickly the electrical impulse travels along the nerve. NCV is calculated by measuring the time it takes for the impulse to travel between the stimulation and recording points.
- Amplitude: This measures the strength of the electrical response generated by the nerve.
6. Sensory Nerve Conduction:
- For sensory nerve conduction studies, the nerve is usually stimulated at a point where the patient feels a sensory response (tingling or twitching). The recorded response reflects the sensory nerve’s ability to conduct signals.
7. Motor Nerve Conduction:
- For motor nerve conduction studies, the nerve is stimulated at a point where it controls muscles. The recorded response reflects the motor nerve’s ability to stimulate muscles.
8. Multiple Nerves:
- NCS can be performed on multiple nerves during a single session, depending on the clinical indications and the suspected areas of concern.
9. Types of Nerve Conduction Studies:
- Different types of NCS can be conducted based on the specific nerves being evaluated, including sensory nerve conduction studies and motor nerve conduction studies.
