Brain and ENT Clinic – Dr Lalit Mahajan In Nagpur & Dr Rachna Gangwani Mahajan In Nagpur
Sinusitis
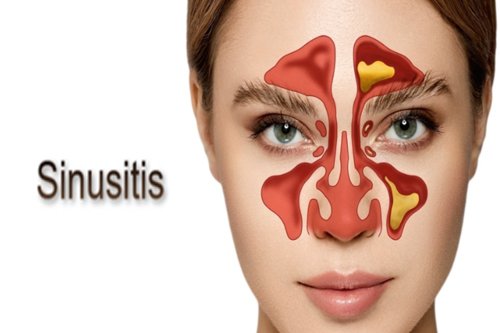
Sinusitis is the inflammation or swelling of the tissues lining the sinuses. The sinuses are air-filled spaces in the bones of the face and skull that are connected to the nasal cavity. When the sinuses become blocked and filled with fluid, it creates an environment where bacteria, viruses, or fungi can grow, leading to an infection.
Acute Sinusitis: This type typically lasts for a short duration, often following a cold or upper respiratory infection. Symptoms may include facial pain or pressure, nasal congestion, and a runny nose.
- Subacute Sinusitis: This type lasts longer than acute sinusitis but less than chronic sinusitis, usually between four to twelve weeks.
- Chronic Sinusitis: This form involves persistent inflammation and symptoms lasting longer than twelve weeks. Symptoms may be less severe than in acute sinusitis but can be more challenging to treat.
Symptoms of Sinusitis
- Facial pain or pressure
- Nasal congestion
- Discolored nasal discharge
- Loss of smell
- Cough and congestion
- Headache
- Fatigue
Treating Sinusitis
Home Remedies:
- Nasal Irrigation: Use a saline solution or a neti pot to flush out mucus and irritants from your nasal passages.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to help thin mucus and keep the respiratory system hydrated.
- Warm Compress: Apply a warm compress to your face to alleviate facial pain and sinus pressure.
Over-the-Counter Medications:
- Decongestants: These can help reduce nasal congestion, but they should not be used for more than a few days as prolonged use may worsen symptoms.
- Pain Relievers: Non-prescription pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Prescription Medications:
- Antibiotics: If the sinusitis is bacterial, a healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics. However, antibiotics are not effective for viral sinusitis.
- Nasal Steroids: These can help reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and alleviate symptoms.
Other Medical Interventions:
- Allergy Treatment: If allergies are contributing to sinusitis, allergy medications or immunotherapy may be recommended.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: Prescription-strength nasal corticosteroids can be more effective in reducing inflammation than over-the-counter options.
Surgery:
- In some cases, surgery may be recommended, especially for chronic or recurrent sinusitis. This could involve procedures to correct structural issues, remove nasal polyps, or open blocked sinus passages.
